In a quiet operating room at the University of Michigan, a team of neurosurgeons made history. For the first time, a patient undergoing epilepsy surgery had a brain-computer interface (BCI) device, called the Connexus, implanted and removed in a swift 20-minute procedure. This milestone marks a bold step forward in the quest to connect human brains directly to computers.
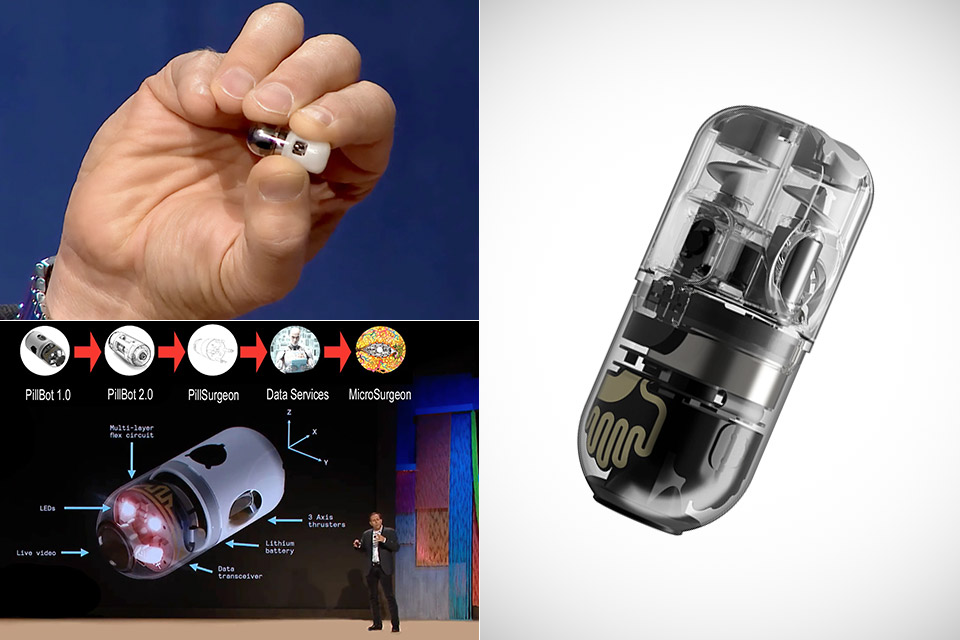

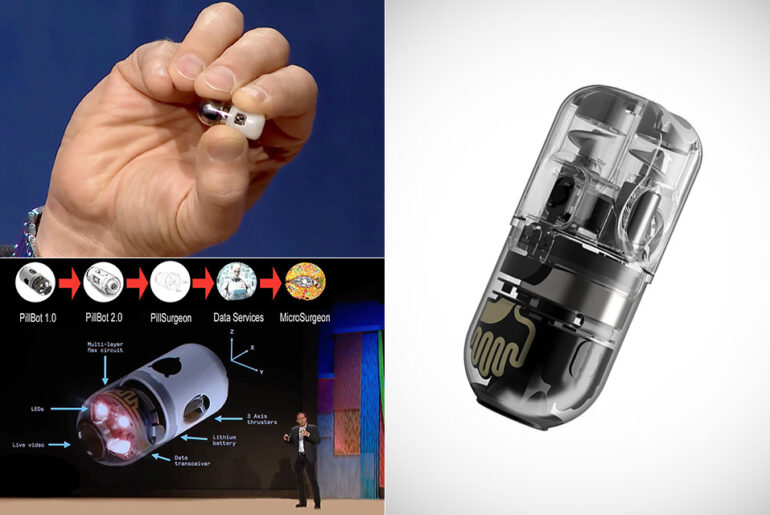
Endiatx’s PillBot drone begins clinical trials, and could one day be used for microsurgery once FDA approval is granted. It’s currently touted as a “moving eyeball in the stomach”, or a pill camera that you swallow, granting access the world’s best GI doctors without ever having to leave home.

Sony makes televisions, game consoles, laptops, and more, but how many knew the company also delves in microsurgery assistance robots? Not only can this machine automatically switch between tools, but it’s designed for surgeons to operate on extremely small blood vessels and nerves, even those measuring less than 0.04 inches.

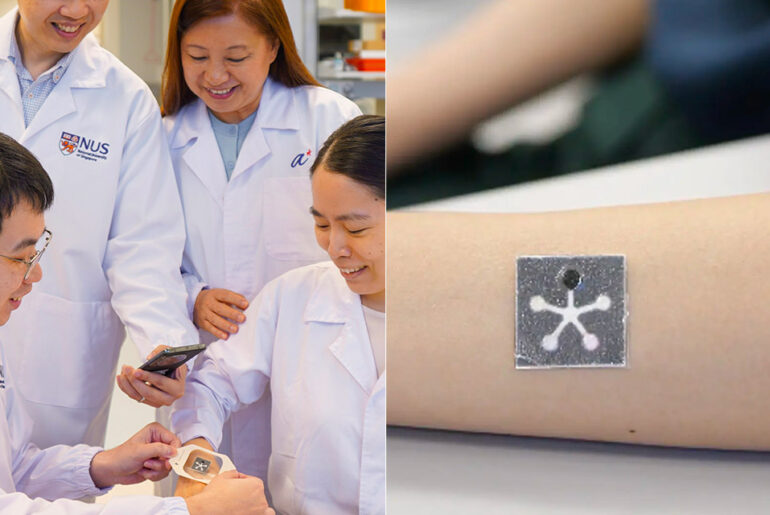
You’ve seen Stanford’s wireless smart bandage that speeds up wound healing, now check out the battery-free PETAL (Paper-like Battery-free In situ AI-enabled Multiplexed) sensor patch by researchers from the National University of Singapore (NUS) and A*STAR’s Institute of Materials Research and Engineering (IMRE). It doesn’t need an energy source because the images are captured by a smartphone and then analyzed by AI algorithms to optimize wound healing.

An endoscopy isn’t the most enjoyable procedure, but AnX Robotica’s NaviCam video capsule pill makes things a lot easier for the doctor and patient. Instead of an endoscope being inserted into the digestive system, this new system has the patient swallowing a pill, which is then controlled via an external magnet and handheld video game style joysticks to move it in three-dimensions inside the stomach.

Harvard researchers have developed a smartphone-assisted ankle exosuit that is designed for use in community settings and could help stroke survivors. This assistive robotic device can help improve their walking speed, distance, propulsion, and gait symmetry. Unlike similar offerings, this one utilizes an active dorsiflexion actuator and has a passive material that flexes like a spring, helping the toes stay up during the foot’s swing phase to prevent the wearer from catching their toes on the ground.
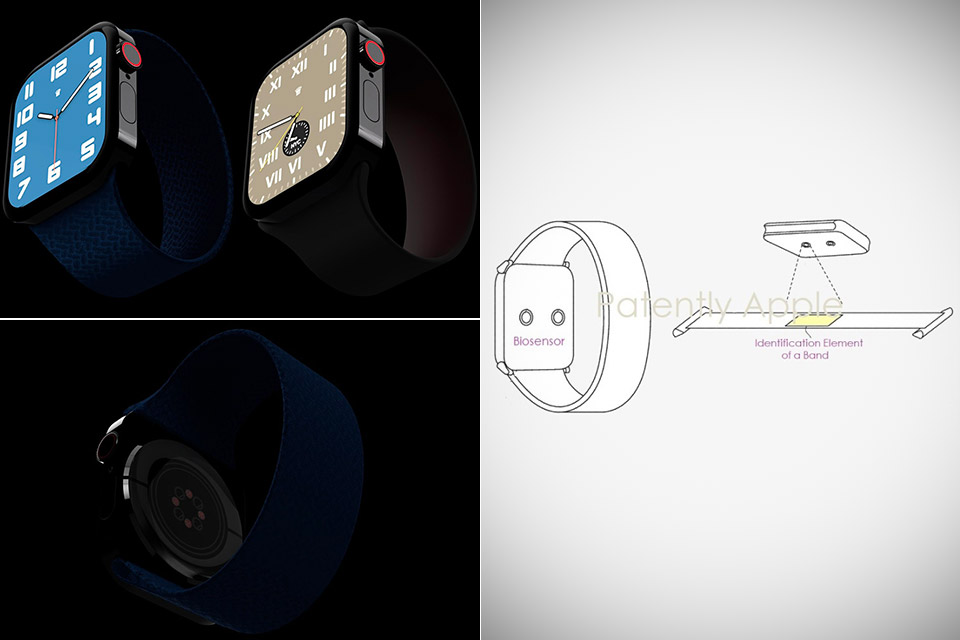
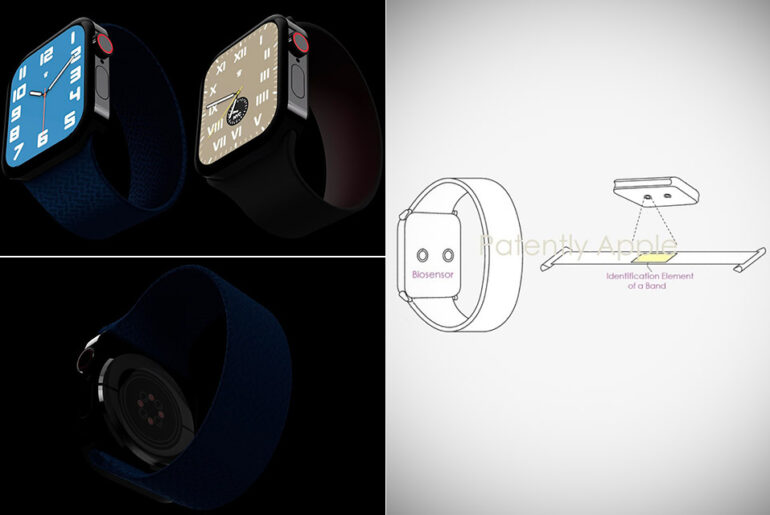
Photo credit: Patently Apple
Color-changing bands are great for aesthetics, but an Apple Watch smart band with health monitoring sensors could save your life. A recently approved patent filing may have leaked such an accessory and an embedded identification element would be used to communicate with the Apple Watch.
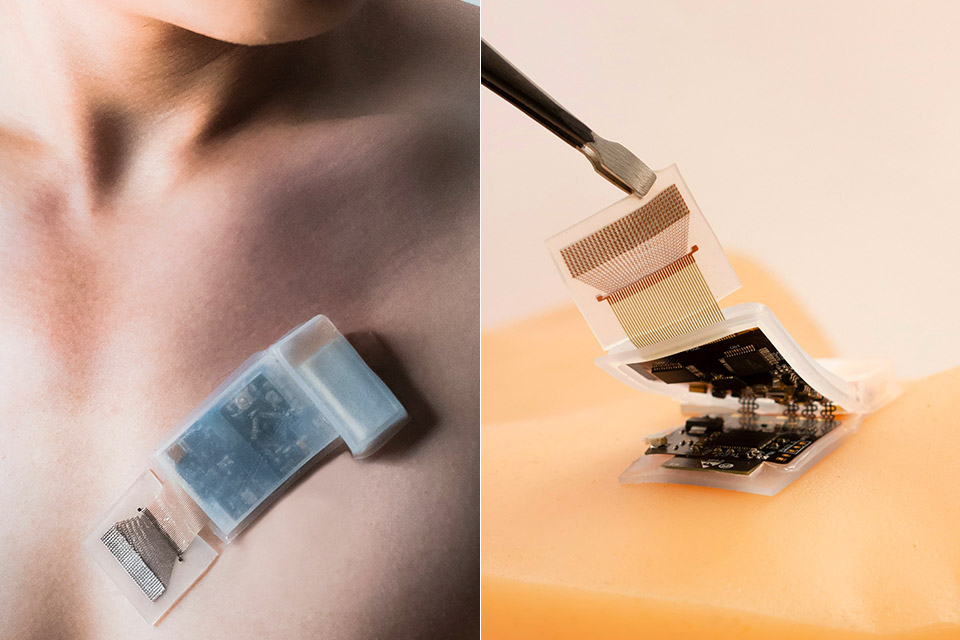
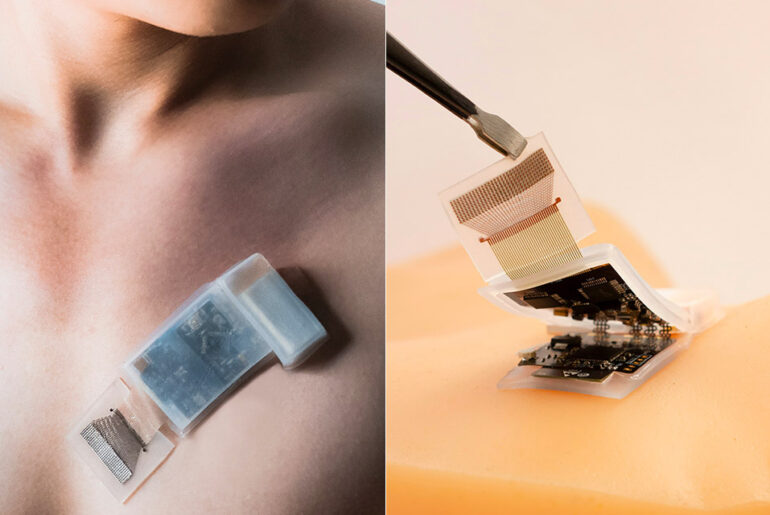
UC San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering researchers have developed a wireless wearable ultrasound patch that could be a game changer for real-time monitoring. This ultrasound fully integrated autonomous wearable ultrasonic system-on-patch (USoP) includes a small, flexible control circuit that communicates with an ultrasound transducer array to collect and transmit data wirelessly.
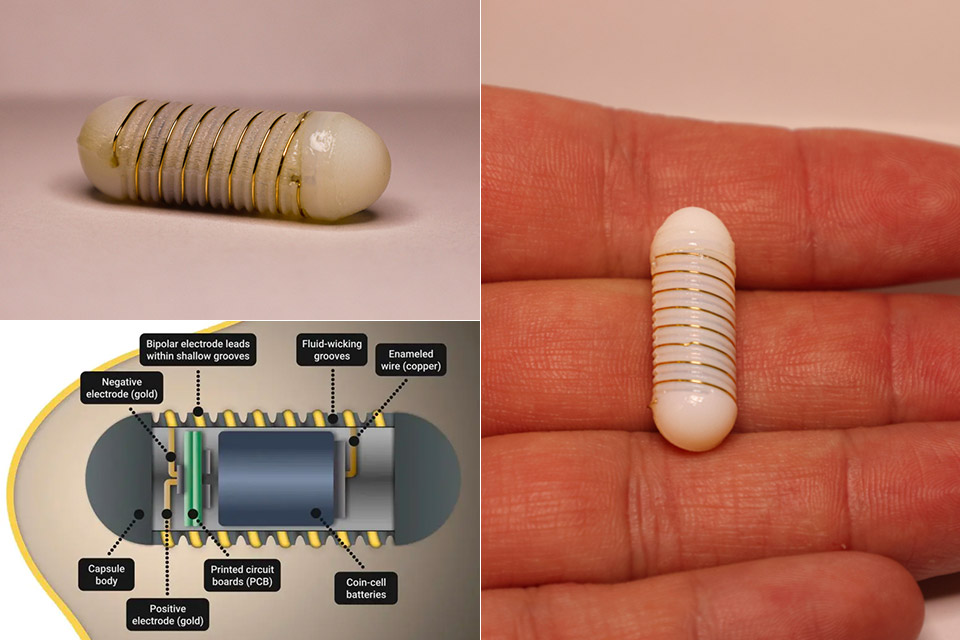
MIT researchers have developed an ingestible electroceutical FLASH capsule that can increase or decrease appetite by stimulating hunger-regulating hormones. They tested it on animals and discovered that this electrical stimulation therapy boosted ghrelin production in their stomach. This suggests that the approach could eventually be adapted to deliver electrical stimulation to other parts of the GI tract.