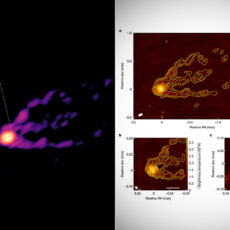
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has found the most distant active supermassive black hole yet in the galaxy CEERS 1019. It is theorized to have existed just 570 million years after the Big Bang and its black hole weighs about 9 million solar masses, which is far less than other black holes that also existed in the early universe.

CEERS 1019’s black hole is more similar to the black hole at the center of our Milky Way galaxy, which is 4.6 million times the mass of the Sun. Why? It’s not as bright as the more gargantuan supermassive black holes previously detected. Since it existed so much earlier, astronomers have a difficult time determining how it formed so soon after the universe began.
- High Magnification: The telescope equipped with 2 eyepieces(H20mm and H6mm) and a 3X Barlow lens. The 3x Barlow lens trebles the magnifying power of...
- 70mm Large Aperture: The refractor telescope is equipped with a large 70mm objective lens and the lens is fully coated with high transmission...
- Wireless Remote & Phone Adapter: Our telescope is equipped with a wireless remote and phone adapter. Just install your mobile phone on the phone...

Until now, research about objects in the early universe was largely theoretical. With Webb, not only can we see black holes and galaxies at extreme distances, we can now start to accurately measure them. That’s the tremendous power of this telescope,” said Steven Finkelstein, Associate Professor of Astronomy at the University of Texas at Austin.