Photo credit: DLR-E. Hellerslien
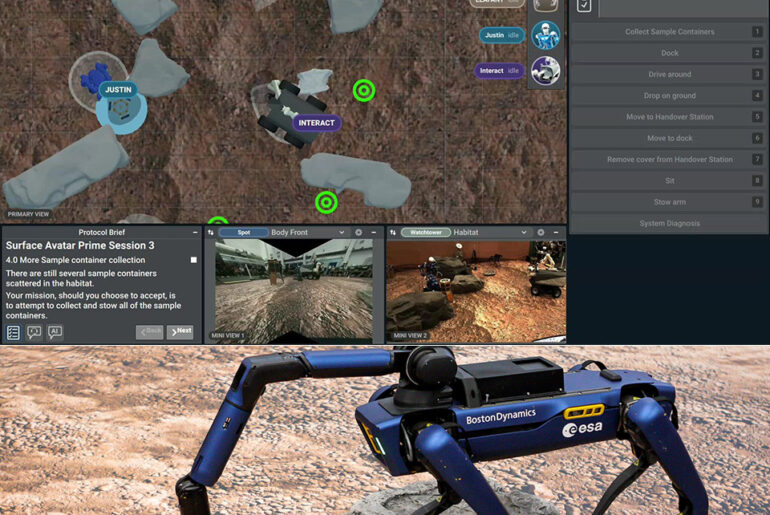
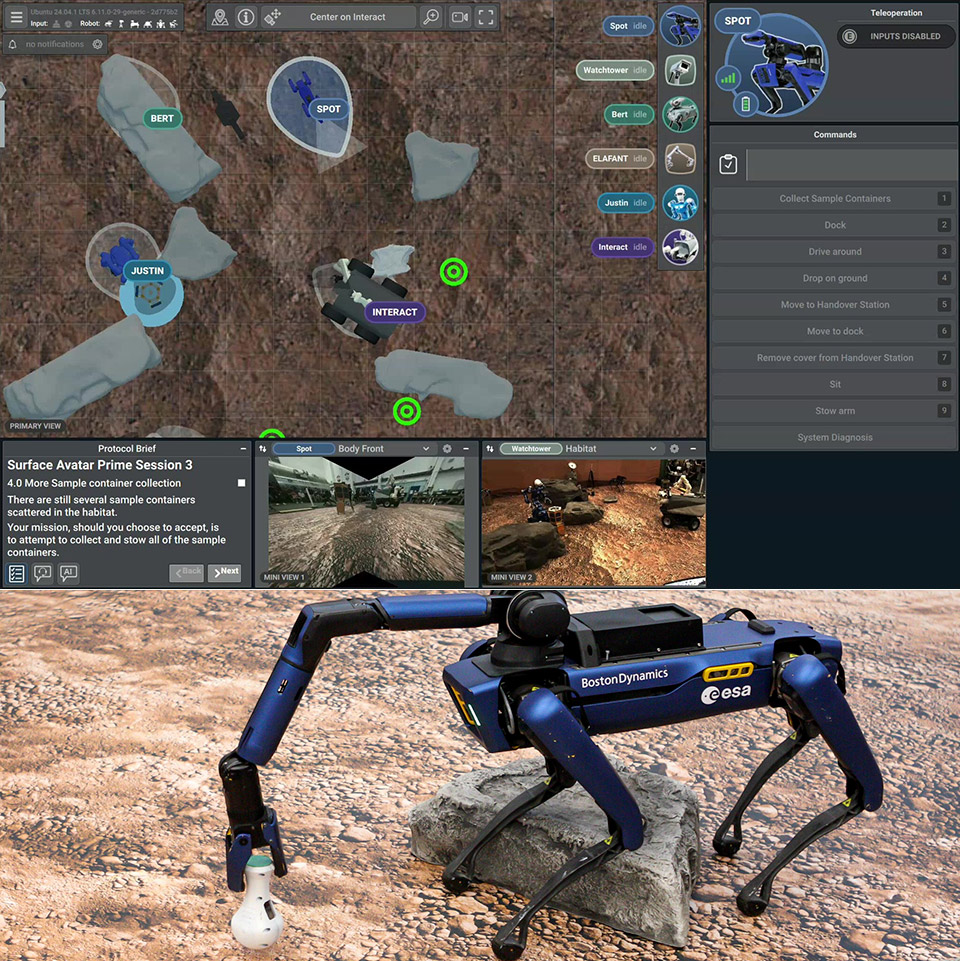
A crimson landscape that resembles Mars’ surface can be found in a rural area in Germany. Jonny Kim, a NASA astronaut aboard the International Space Station, leaned into a custom interface, his hands on a joystick and a haptic device, preparing to lead a team of robots in this foreign environment. The Surface Avatar project, a collaboration between the European Space Agency (ESA) and the German Aerospace Center (DLR), concluded with this session. What exactly is the goal? To perfect astronauts’ ability to control robotic teams on far away worlds like the Moon or Mars from orbit.
Kim controlled four robots: ESA’s Interact rover, Boston Dynamics’ Spot, DLR’s humanoid Rollin’ Justin, and another robot dog, Bert. Each played a role in two tough scenarios designed to test their skills. The first scenario required Spot and Justin to collect scattered sample containers from the rough terrain. Spot moved on its own, dashing around to find and grab containers before bringing them to a handover station. Kim then controlled Justin to transport the samples to a lander, using a combination of direct control and pre-programmed commands. Spot even had to recognize and modify a cover on the sample station it needed to grab. When it messed up the grab, it acknowledged the error, changed and succeeded, showing a new level of self-correction.
- 2 AVIATION LEGENDS, 1 BUILD – Recreate the iconic Boeing 747 and NASA Space Shuttle Enterprise with the LEGO Icons Shuttle Carrier Aircraft (10360)...
- DEPLOY LANDING GEAR – Turn the dial to extend the massive 18-wheel landing system on your airplane model, just like real flight operations
- AUTHENTIC FEATURES & DETAILS – Remove the tail cone, engines, and landing gear from the NASA shuttle and stow them in the cargo bay during flight
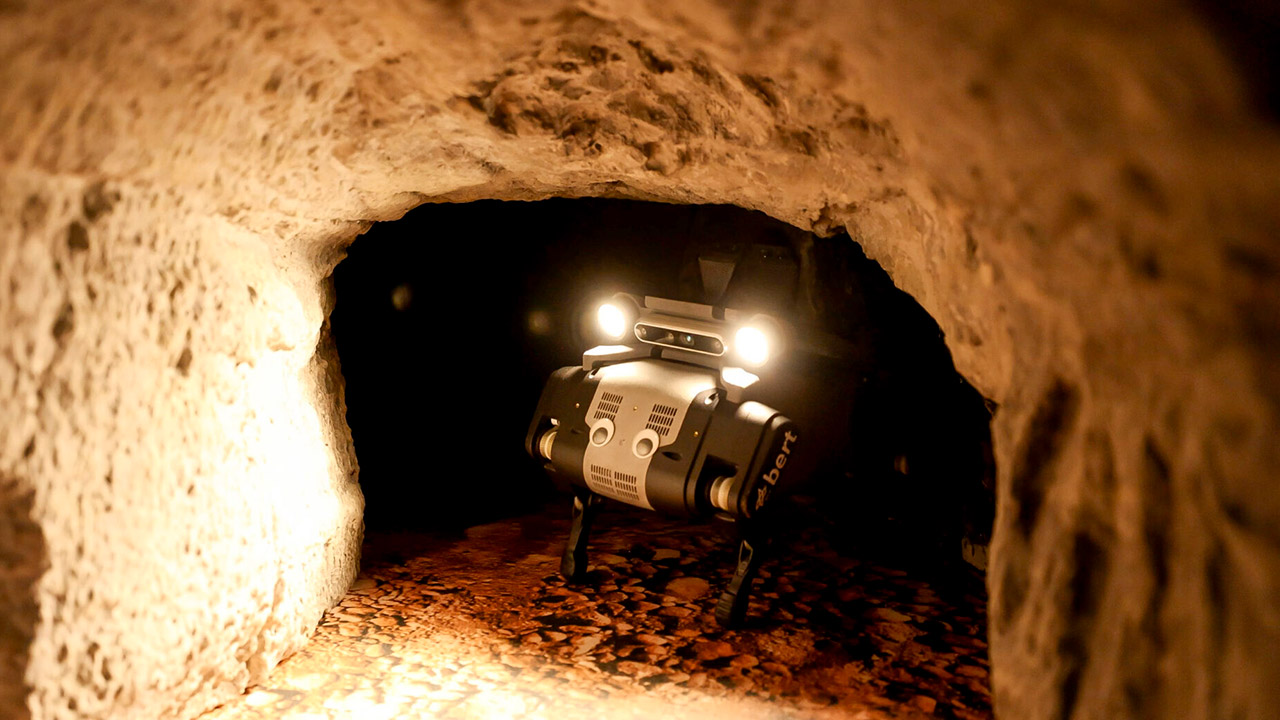

The second scenario went underground, starting with the Interact rover taking Bert to a cave entrance blocked by a boulder. Kim used Interact’s robotic arm to clear the obstacle and deploy Bert. However, Bert’s leg malfunctioned after landing. So, Kim had to retrain its walking algorithm in real time, adapting to the glitch before Bert could explore the cave and find signs of Martian ice.
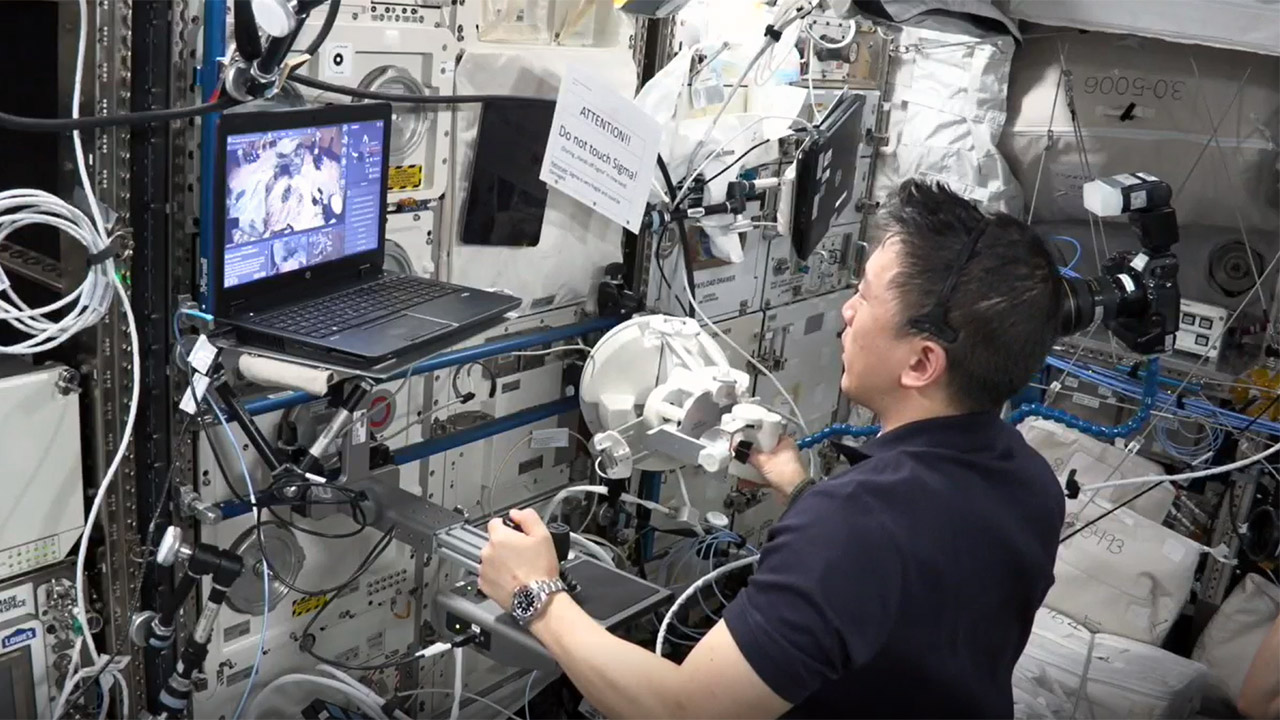

It’s a joystick, haptic feedback and dual-view display built by ESA and DLR that switches between a robot’s eye view and a top-down map. ESA’s Rute Luz, who designed the interface, drew inspiration from real-time strategy games. Kim can control one robot directly and assign tasks to others, a big step up from when every move had to be done by a human. He adapted quickly, the design is intuitive. On the ground the sample tubes – designed to stay upright no matter how they’re handled – allowed the robots to work flawlessly. Behind the scenes ESA’s Nicole Roshardt kept the link between the ISS and Earth stable.
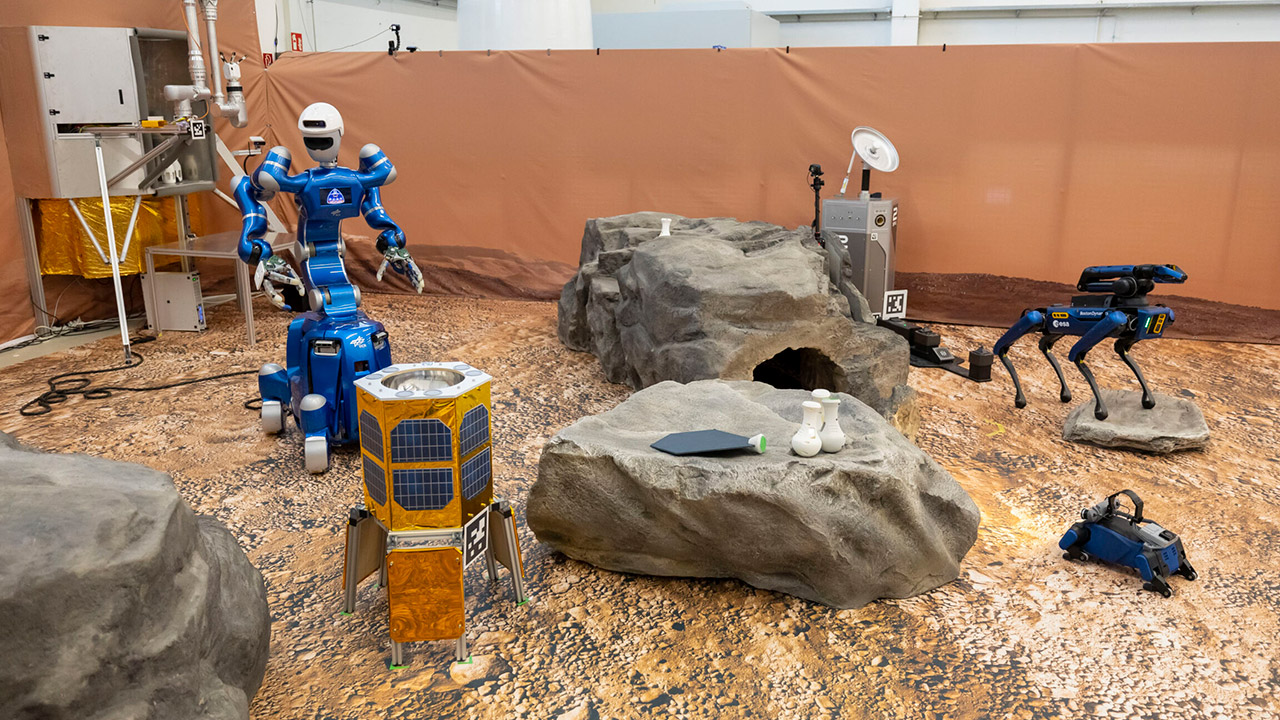

Surface Avatar has gone through four sessions, each one building on the last. From Samantha Cristoforetti’s first test in 2022 to Kim’s run in 2025 the project has refined how humans and robots work together. Each session added complexity – more autonomy, tougher tasks and realistic challenges like equipment failure. ESA’s Benoit Pouffary who leads the project’s studies sees this as the foundation for Europe’s role in future lunar and planetary missions. Being able to delegate tasks to robots while keeping humans in the loop could change the way we explore space.
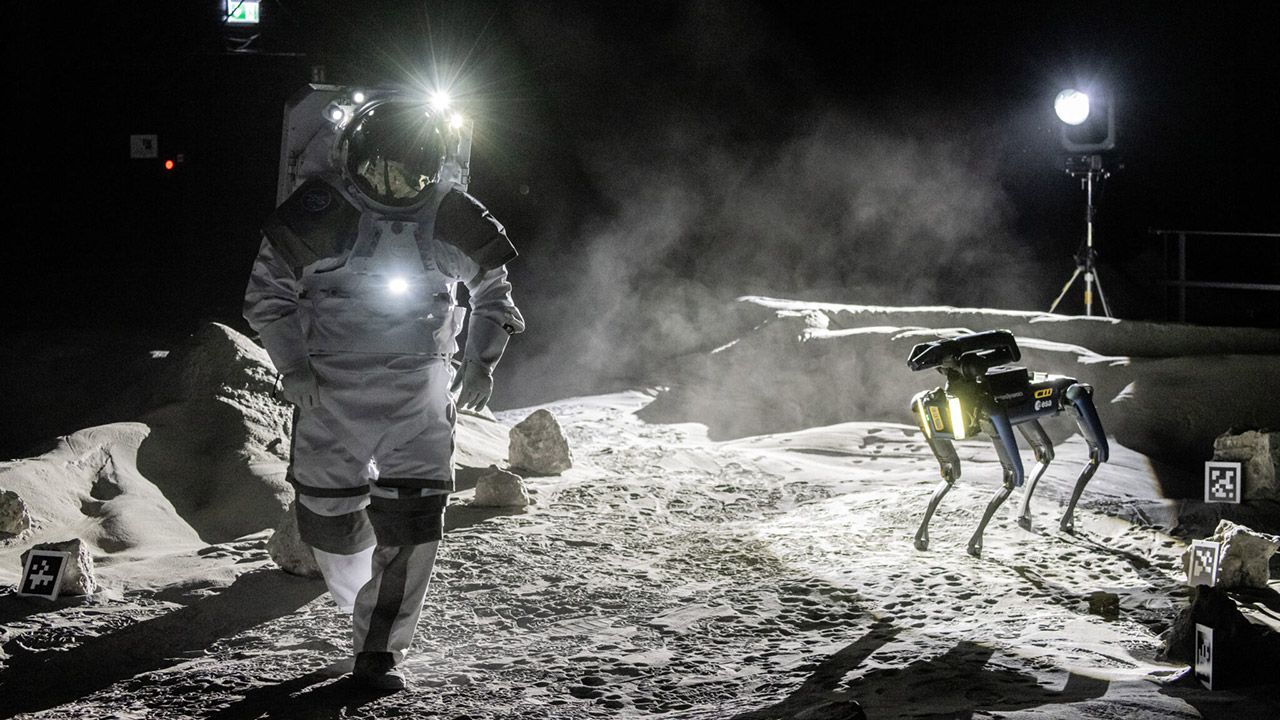

The next phase will go to ESA’s LUNA facility, a lunar-like testing ground with dusty terrain and simulated spacesuit operations. Spot and Interact will face new challenges, helping to catalog tasks for future Moon missions. There’s even talk of expanding to geology and spectrometry analysis with ESA’s UK site. The haptic controller Kim used is still on the ISS, ready for the next test.