
NASA / ESA’s Hubble Space Telescope captures a jellyfish-like dying star located 5,000 light-years from Earth in nebula NGC 2002. When stars like our Sun grow old, they eventually expand and glow red, effectively turning into a red giant, which then begins to cast off their outer layers of material into space.
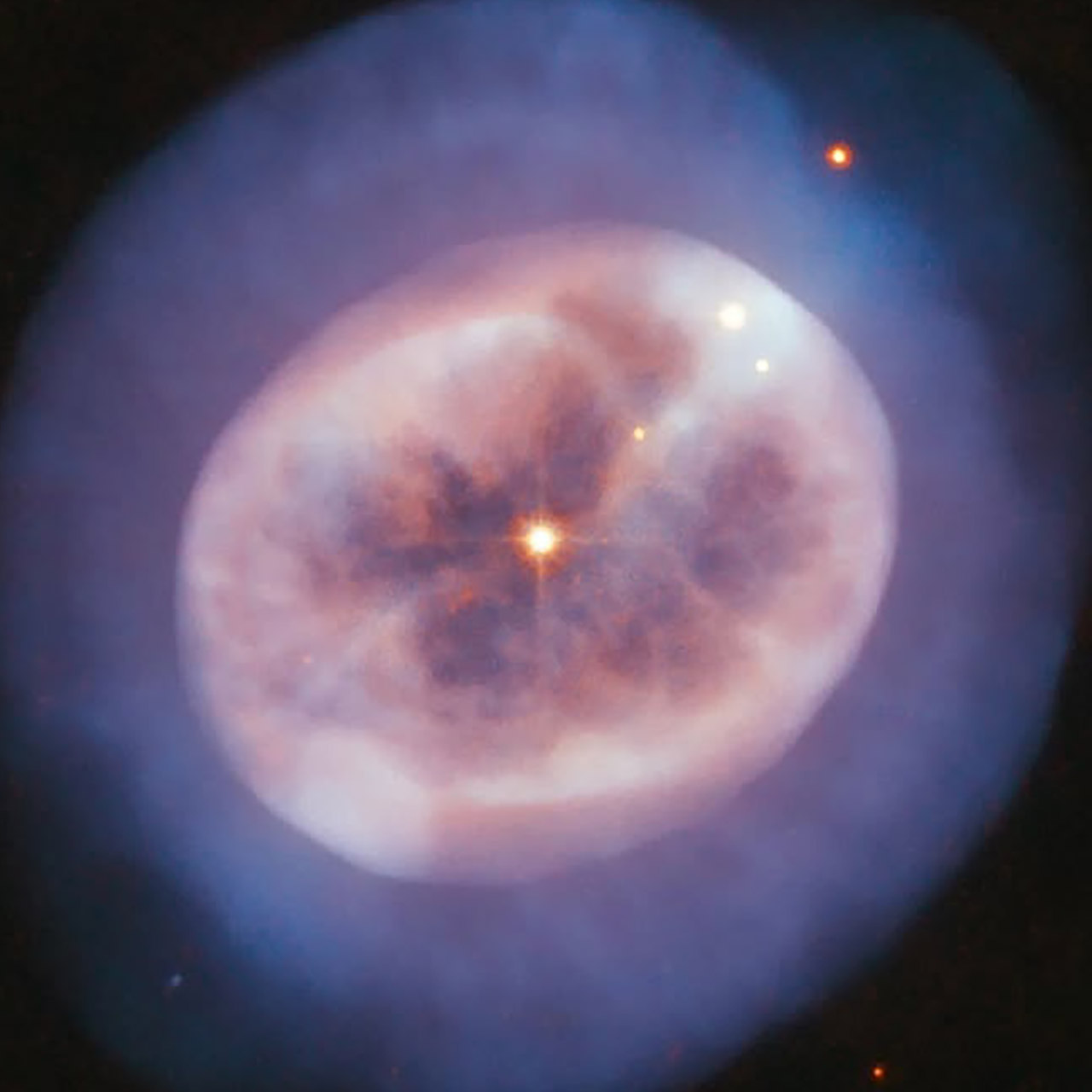
When these red giants are casting off their outer layers, they can lose more than half of their mass, forming a shell of surrounding gas. At the same time, the star’s core shrinks and grows hotter, emitting ultraviolet light that causes the expelled gases to glow like in the image above. More specifically, we can observe a bright reddish point of light surrounded with shells of gas and dust, while an inner circle of gas appears pale red, with a hazier ring of bluish cosmic material enveloping it.
- Superior Optics: 400mm(f/5.7) focal length and 70mm aperture, fully coated optics glass lens with high transmission coatings creates stunning images...
- Magnification: Come with two replaceable eyepieces and one 3x Barlow lens.3x Barlow lens trebles the magnifying power of each eyepiece. 5x24 finder...
- Wireless Remote: This refractor telescope includes one smart phone adapter and one Wireless camera remote to explore the nature of the world easily...
NGC 2002 contains about 1,100 stars. The more massive stars in the cluster tend to sink inwards towards the center, while the lighter stars move away from the center as the cluster evolves,” said the NASA Hubble Mission Team.
















