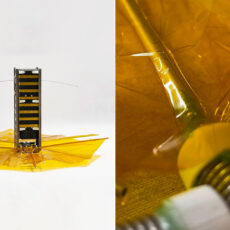
Photo credit: Kyoto University
JAXA’s (Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency) LignoSat was successfully deployed from the International Space Station in December 2024. Researchers are using it to investigate the use of wood in space and the findings could one day offer a more sustainable alternative to conventional satellites.
Sensors on the satellite will be used to evaluate strain on the wood and measure its responses to temperature and radiation in space. Geomagnetic levels can be used to determine whether the geomagnetic field can penetrate the body of the wooden satellite and interfere with its technological capabilities. The data gathered from space could lead to innovative solutions for future astronauts.
- 3 LEGO space toys in 1 box – Boys and girls ages 9 and up who love space can build and rebuild 3 different sets using the same set of bricks with...
- Endless space play possibilities – Kids can play out daring stories among the stars with 3 different space playsets: an astronaut figure, a space...
- Posable space figures – The astronaut toy has posable legs, feet, arms and fingers, and the space dog has a posable tail and legs so kids can choose...

A traditional Japanese wooden joining method, the Blind Miter Dovetail Joint, is used for LignoSat to connect two wooden panels without using glue or nails,” said Andrea Lloyd, International Space Station Research Communications Team.