
For those who don’t already know, Tesla’s Megapacks are being produced at dedicated Megafactories, with the primary one located in Lathrop, California. Now what is a Megapack exactly? It’s essentially a large-scale, rechargeable lithium-ion battery system designed for utility-scale energy storage, capable of storing over 3.9 MWh of energy per unit—enough to power about 3,600 homes for an hour.
The main factory, located in Northern California near Tesla’s Fremont car plant, is one of the biggest utility-scale battery factories in North America. It can make 10,000 Megapacks a year, equal to 40 GWh of energy storage. It’s been running since late 2022 and is now almost at full speed, producing a Megapack every 68 minutes (about 25–28 units a day when fully going). The factory covers around 1 million square feet and uses high-tech methods, including huge industrial robots for building.
- Upgrade Amphibious RC Cars Monster Truck Range : Upgrade the normal Lithium-ion battery to 7.4V/600mah Lithium-ion Ternary Battery *2. Monster truck...
- Waterproof Vehicles Truck Body for All-Terrain: our rc truck is equipped with metal shock absorbers to dampen vibration, strong grip, high quality...
- Long-Range Anti-Interference Design: 2.4GHz full-featured proportional radio control system can be controlled stably within the range of 40 meters...
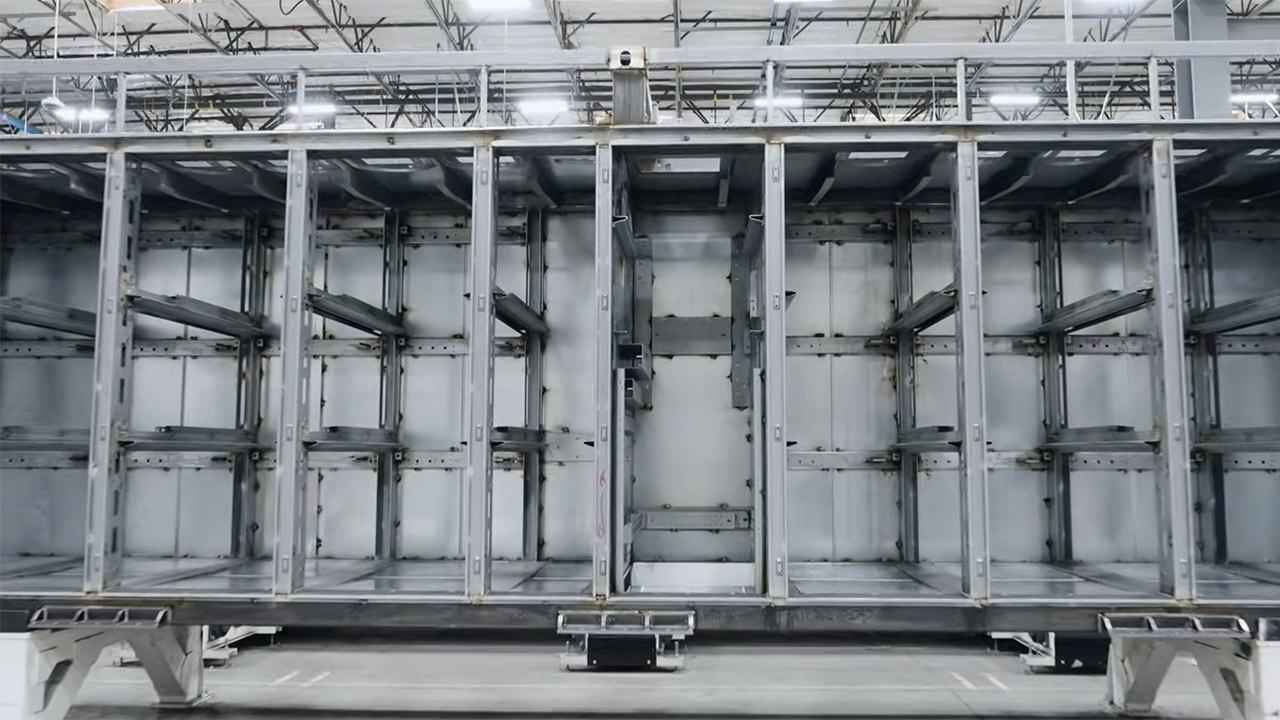
Tesla’s Megafactories are designed for quick setup and growth. The Lathrop factory went from starting construction to making batteries in just over a year, and the Shanghai one did it in eight months—super fast compared to competitors, who might take two years for similar projects. This speed comes from Tesla’s straightforward approach and standard building processes.
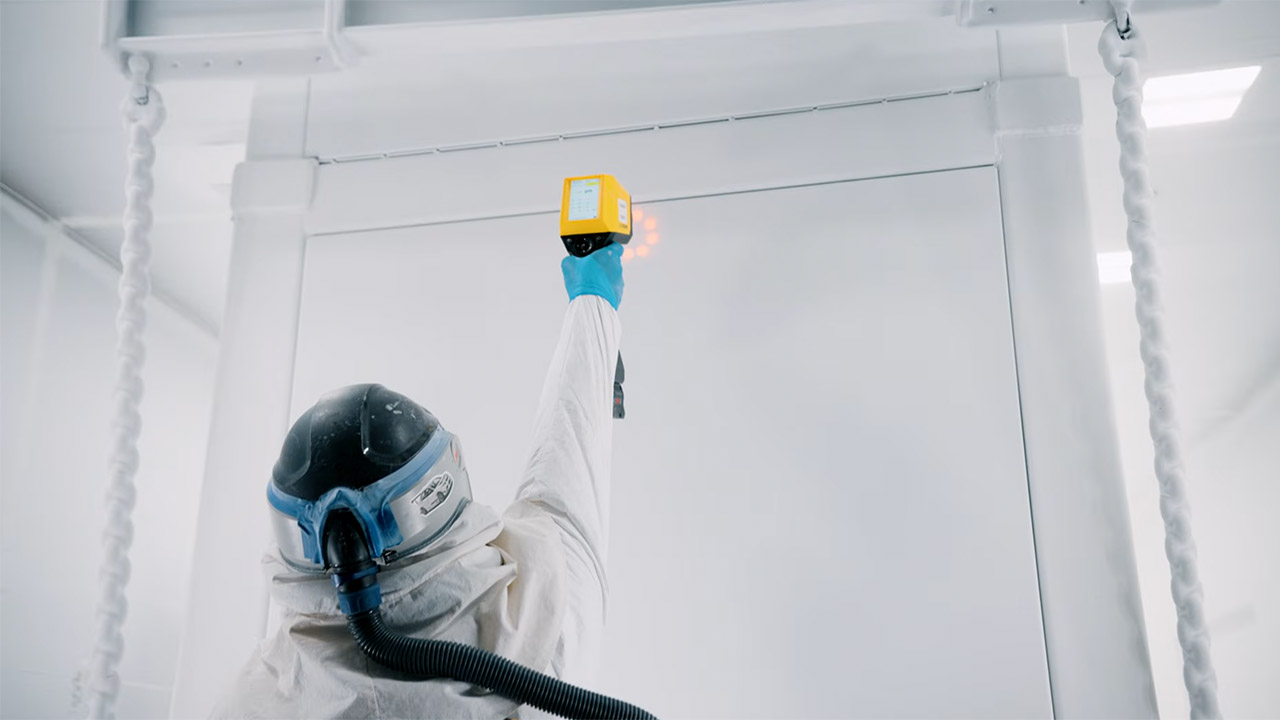

Early on, Lathrop’s production was slowed by a shortage of silicon carbide chips, limiting it to one of two lines (about 16 GWh a year). Tesla’s deal with CATL, a Chinese battery maker, keeps a steady flow of lithium iron phosphate (LFP) cells, which are cheaper and tougher than regular NMC batteries. Elon Musk says demand for Megapacks is “almost endless,” with new orders waiting until mid-2025 for delivery.
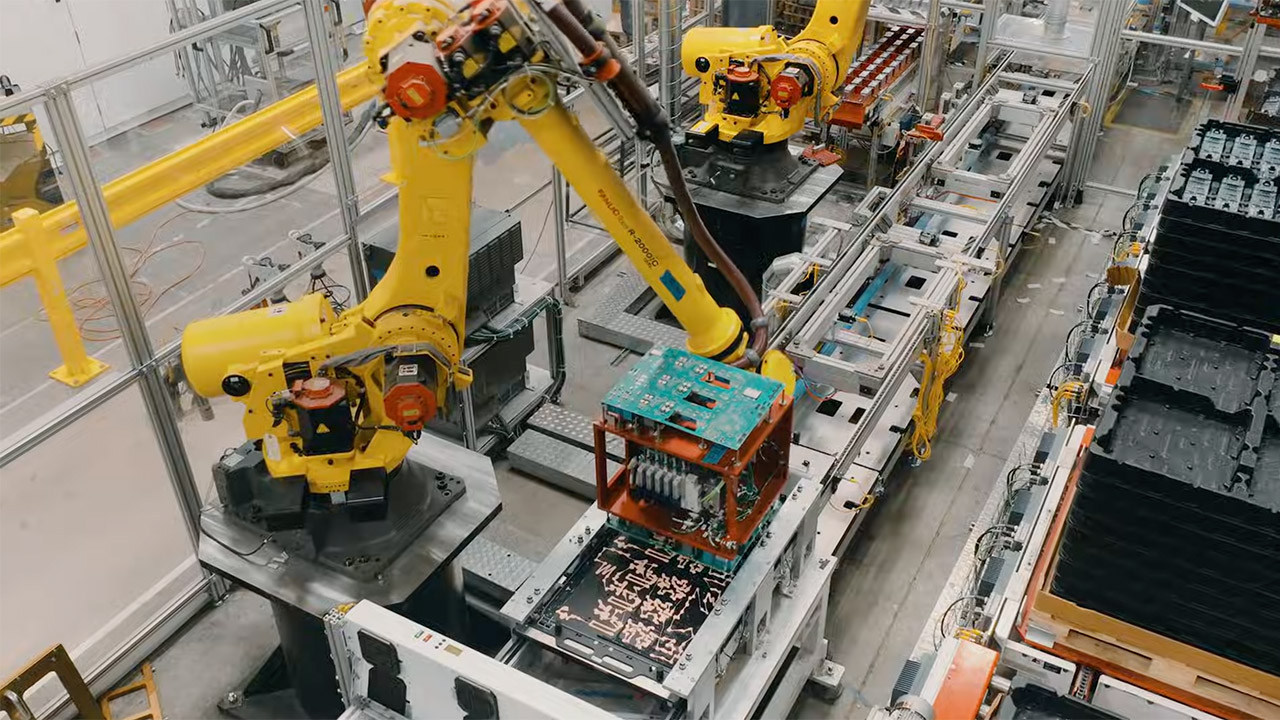

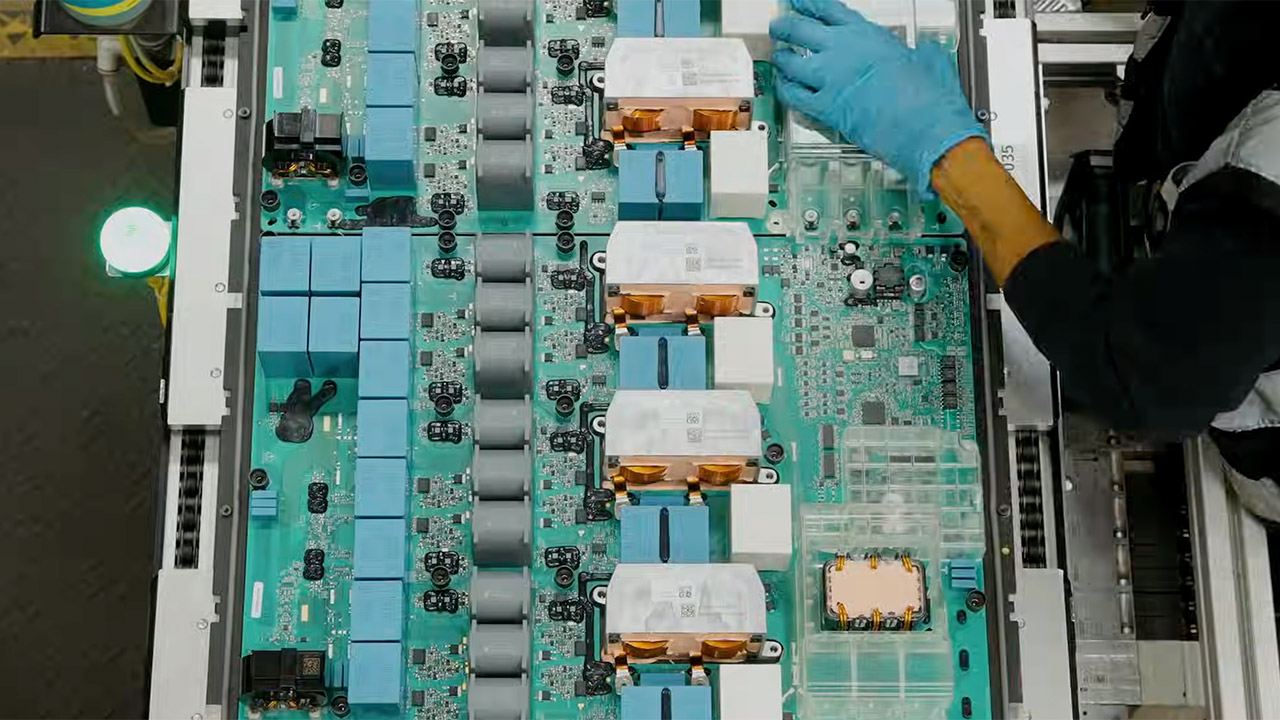
The Lathrop and Shanghai Megafactories use high-tech industrial robots for jobs needing great accuracy and speed, like putting together battery modules, adding inverters, and moving heavy parts. Big robotic arms, like those in Tesla’s car factories, handle repeating tasks such as welding, stacking cells, and shifting large pieces of the Megapack, which weighs about 38 tons each. These robots make production smoother, letting the Lathrop factory produce a Megapack every 68 minutes when running at full speed.
The Megapack’s design is “endlessly scalable,” so it can be tailored for projects of any size, from 46 MW rural grids in Alaska to 350 MW giant projects like the Victoria Big Battery in Australia. This versatility lets Tesla use thousands of units for all kinds of needs.
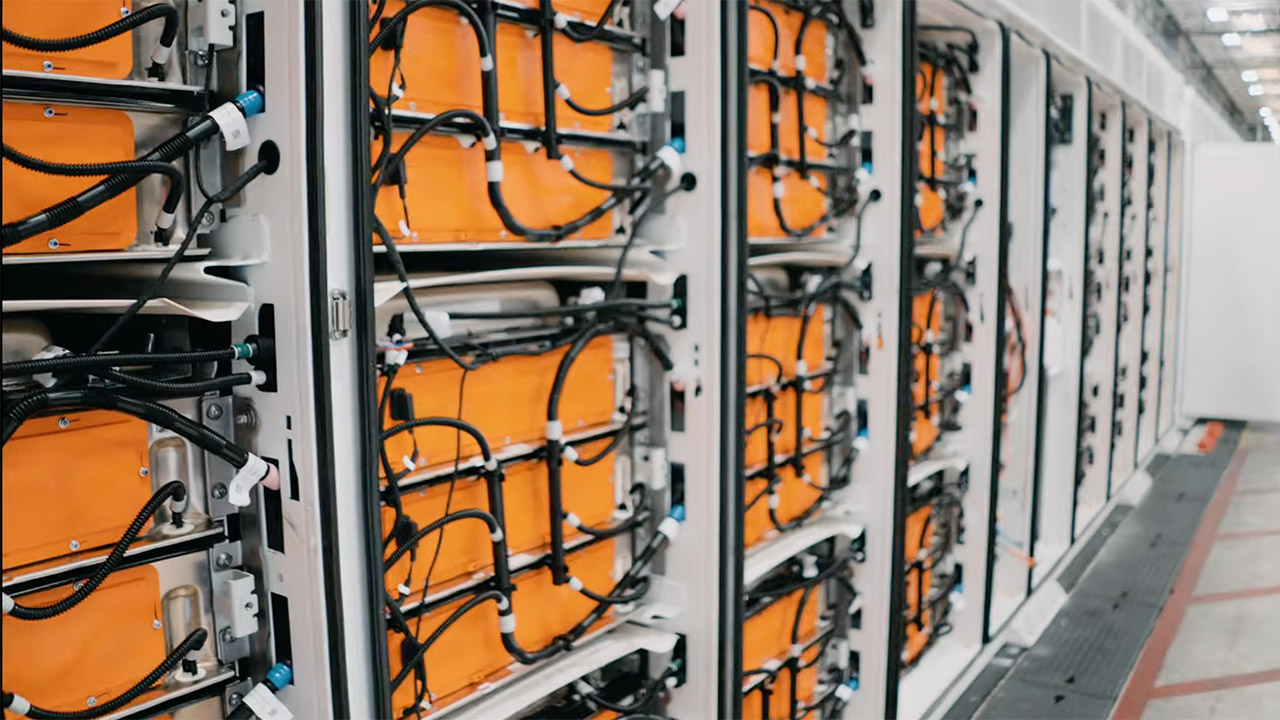

Tesla’s Master Plan Part 3 says the world needs 240 TWh of energy storage for a fully green grid, which would take about 55 more Megafactories at the current 40 GWh per factory rate. The Texas factory is part of this plan, and Tesla’s success in copying its Megafactory model globally (like in Shanghai) shows more growth is possible.










