The Operational Land Imager (OLI) on NASA / USGS’s Landsat 8 satellite captured a stunning image of Italy’s Mount Vesuvius peeking through a sea of clouds. Upon closer inspection, we can clearly see the ridge surrounding the cone, a remnant of the collapsed caldera of an older volcano, Mount Somma, from which the cone of Vesuvius emerged.

Why is Mount Vesuvius relevant today? Well, scientists know that the mountain has had eight major eruptions in the past 17,000 years by dating lavas. The most recent eruption on March 17, 1944 destroyed the village of San Sebastiano, and since then, it has experienced occasional earthquake activity, ground deformation, and gas venting from the crater.
- Milky Way wall art décor – Create a large Milky Way Galaxy piece of art with this LEGO building kit for adults
- LEGO 3D-effect wall décor – A Milky Way Galaxy artwork created from 3,091 layered LEGO bricks and pieces to produce a 3D effect with depth and...
- Packed with features – Wall art includes some of the Milky Way’s most famous stars, clusters and other spectacles, including Trappist-1, The...
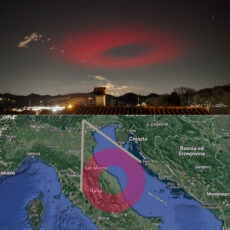
Naples has a population of 3 million people, 800,000 of whom live on the volcano’s slopes. This makes Vesuvius one of the most dangerous volcanoes on the planet. Its most famous eruption, in A.D. 79, destroyed the cities of Pompeii and Herculaneum. The cities were engulfed in pyroclastic flows—superheated, high-density clouds of volcanic gas, ash, and rock that flow downslope at hundreds of kilometers per hour,” said NASA.
[Source]