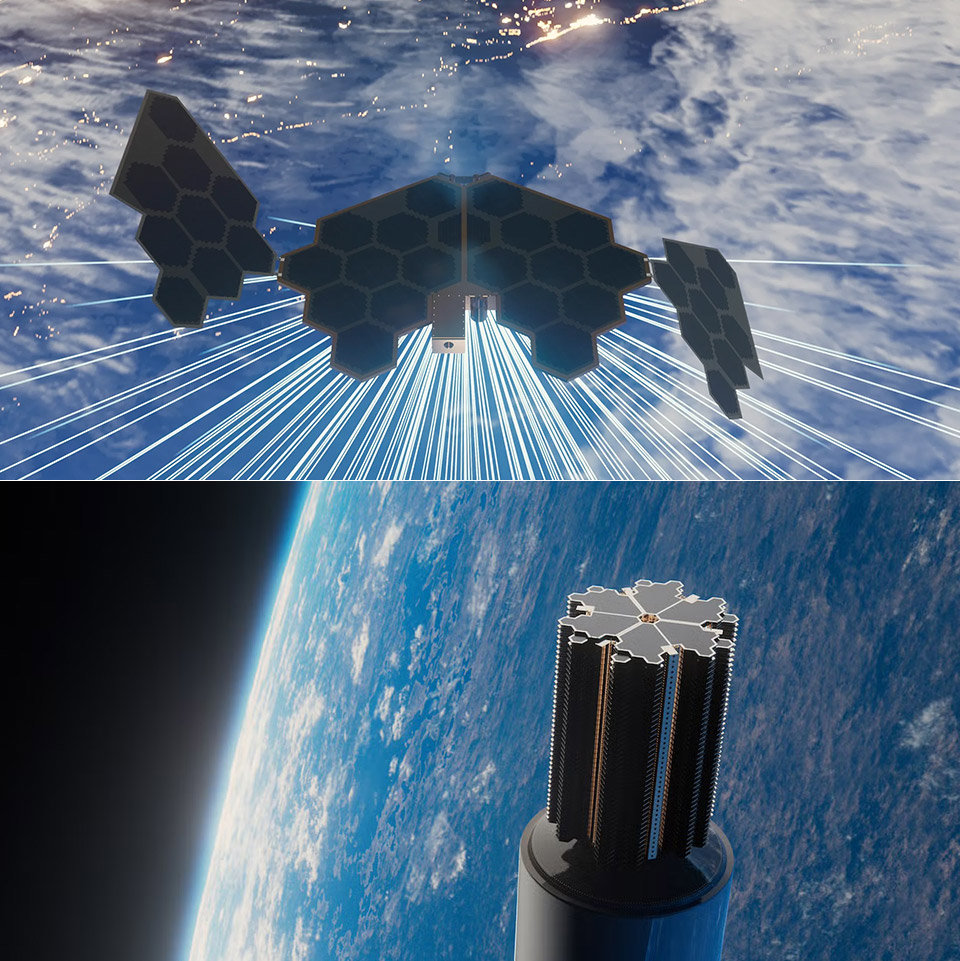
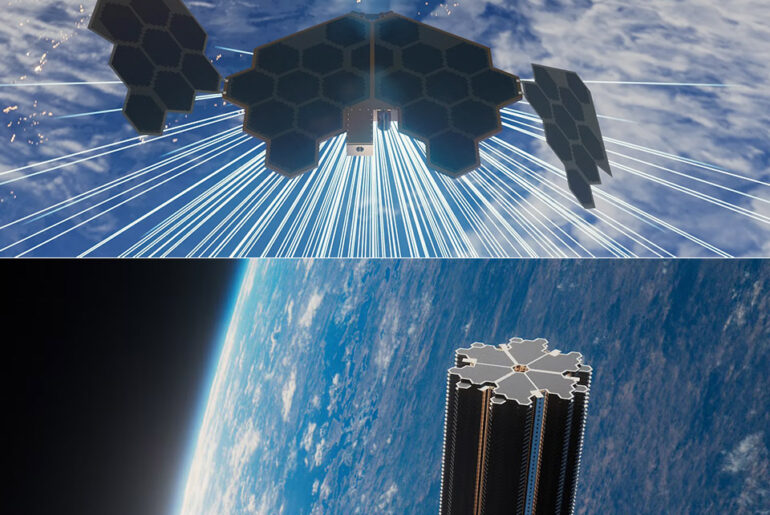
SpinLaunch, the company that used to launch satellites into orbit with a giant centrifuge, is taking on Starlink and Project Kuiper with its Meridian Space constellation. This low-earth orbit (LEO) satellite network will deliver high-speed internet to businesses worldwide. With $30 million in new funding, a partnership with Kongsberg NanoAvionics and a target for first customer connections by late 2026, SpinLaunch is making a big move into the satellite broadband market.
Meridian Space is built around 280 microsatellites, each weighing about 70 kilograms – much lighter than traditional communication satellites. These satellites, designed and manufactured by Kongsberg NanoAvionics in a $135 million deal, are the backbone of a network that SpinLaunch claims can deliver over two terabits per second of global bandwidth from a single rocket launch. Unlike the thousands of satellites in other constellations, Meridian’s smaller fleet is designed for efficiency, to provide high-speed internet with fewer spacecraft. The company will scale to 1,200 satellites eventually, but the initial phase is focused on proving the concept with a leaner setup.
- Beyond-fast WiFi 7 (802.11be) with new 320MHz channels in the 6 GHz band and 4096-QAM significantly increases network capacity and throughput, with...
- Multi-link Operation links to multiple bands at the same time to ensure stable internet connections and efficient data transfers
- Cutting-edge external dual-feeding antennas boost coverage by providing high efficiency and significantly enhanced signal strength
Meridian Space’s satellites have fixed-track orbits, which means they repeatedly pass over the same ground locations. This simplifies the design of ground-based user terminals and gateways, eliminating the need for complicated satellite tracking antennas. Businesses can use compact, low-power antennas that can be mounted on rooftops or data centers, lowering the cost and energy requirements for setup. SpinLaunch says this also reduces the risk of collisions in orbit and makes better use of radio spectrum, which is a concern in LEO.
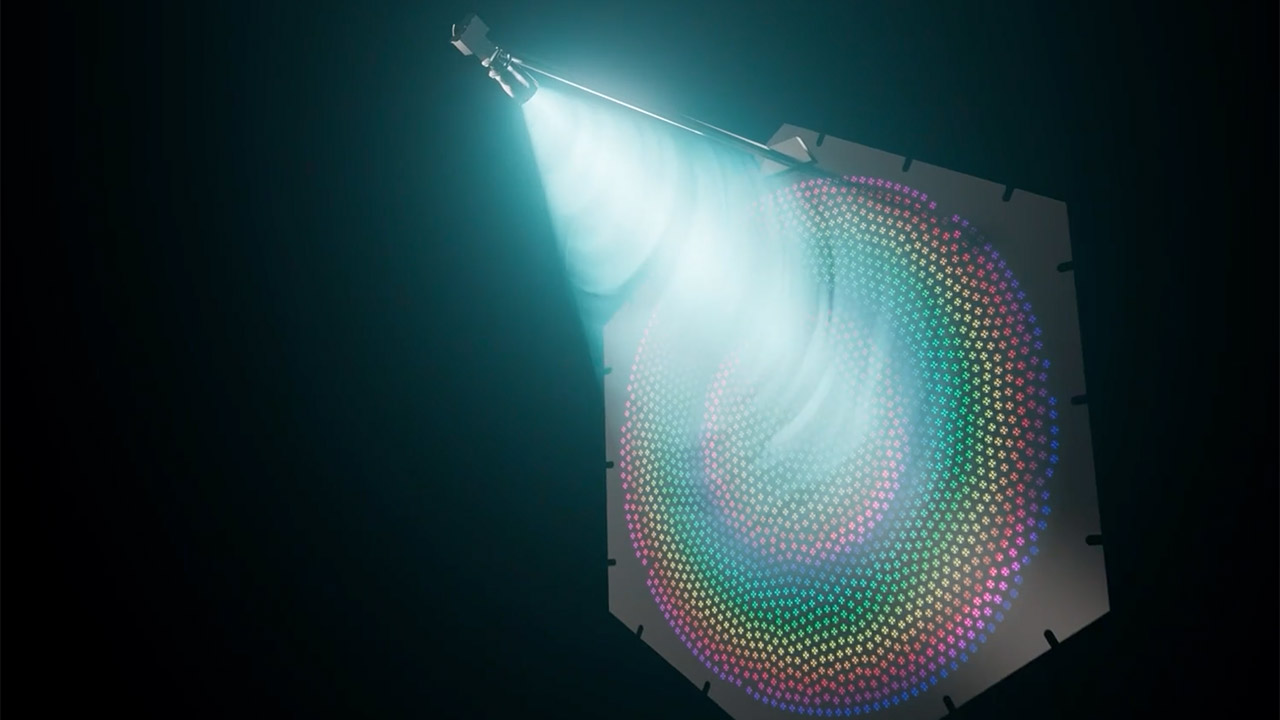
SpinLaunch’s satellites use a new antenna technology called a reconfigurable reflectarray. Unlike traditional satellite antennas which are big and power hungry, these are light, energy efficient and can operate across multiple frequency bands. The company has just completed full scale testing of this antenna, a major milestone that proves it can deliver high performance without the high cost of traditional designs. This means Meridian’s satellites can be smaller and cheaper, reducing the capital expenditure to build and maintain the constellation. David Wrenn, SpinLaunch’s Chief Innovation Officer, calls this a key step to making the network technically and financially viable.
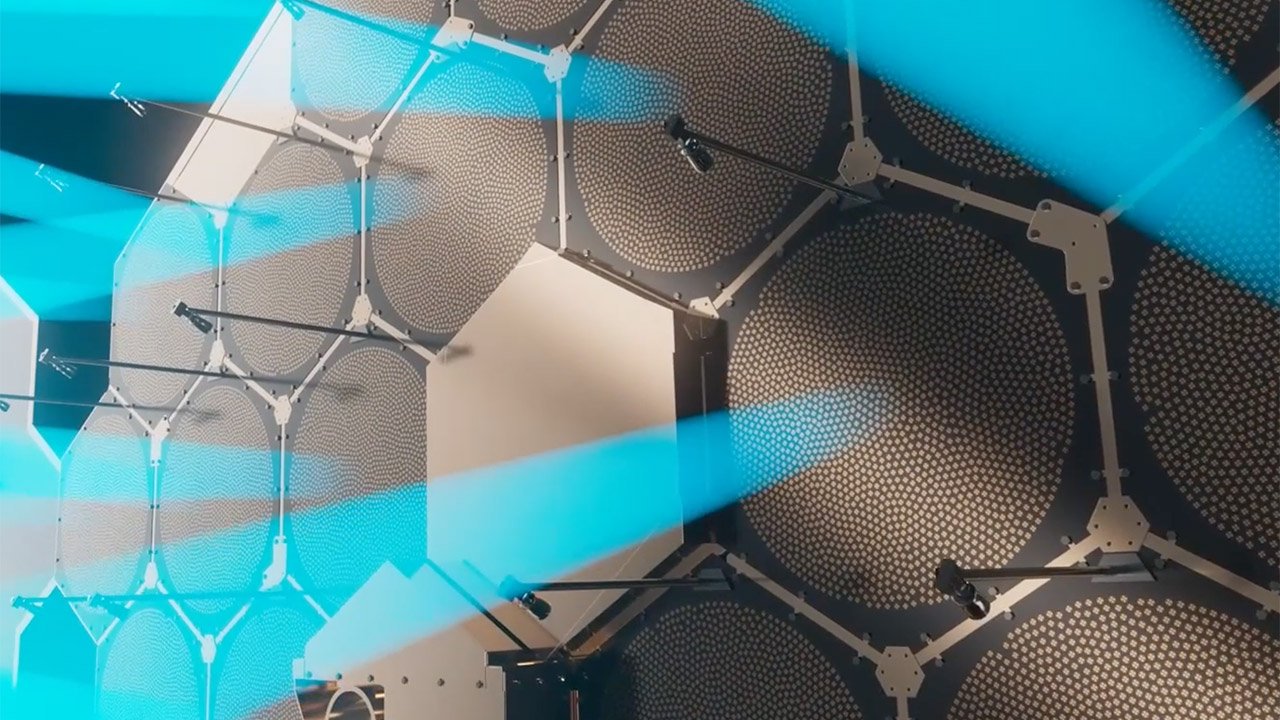

The constellation uses a “bent-pipe” architecture, a simple approach where satellites act as relays, passing signals between ground stations without onboard processing. This reduces the complexity and power requirements of each satellite, making it more reliable and cheaper. By using ground based infrastructure for signal processing, Meridian Space can deliver high speed internet while keeping satellites light. It also uses 5G non-terrestrial network protocols, so it can integrate with modern comms.